Research
The overall aim of this multidisciplinary research and innovation action was to develop a soft, modular, lower limb exoskeleton that people with muscle weakness and/or a partial loss of sensory or motor function could wear to assist their leg strength and support, to increase their mobility, and thereby improve their health and quality of life. XoSoft employed smart soft robotics, biomimetic controlled actuation, and connected health data feedback and interface. XoSoft was:
- A highly customisable modular system, comprising an ankle-foot-knee module that could be worn on one or both sides and a hip module.
- Easy to wear, comfortable, serviceable, and compatible with the daily lives of the users.
- Developed advanced textiles and smart materials to create sensing, variable stiffness joints, and actuation, using technologies such as electro-rheological fluids, and flexible tactile sensors based on polymeric films with carbon nanotubes and nanowires.
- Controlled through biomimetics to identify the user’s motion and intention and to determine and provide the appropriate level of assistance.
- Equipped with integrated health connectivity and analysis features to enable the wearer and their clinicians/therapists to review activity information and to register deterioration of the conditions at an early stage.
- Developed with a user-centred design approach: following extensive testing in the lab, the concept was subject to trials in clinical settings and home environments.
Workplan
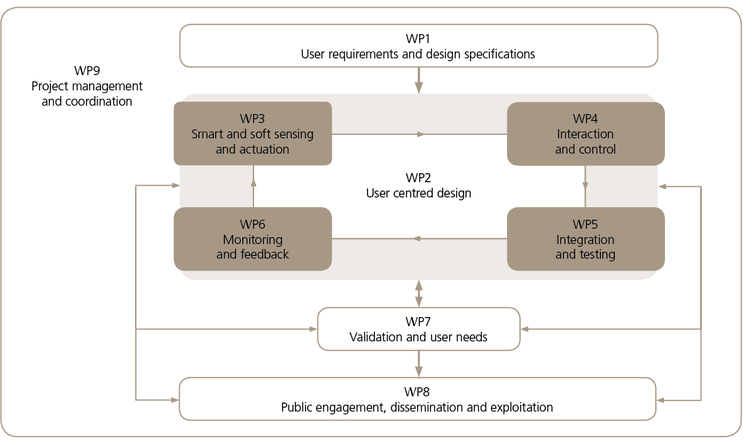
XoSoft’s work plan consisted of nine distinct work packages (WP):
- WP1: User requirements and design specifications
Define user requirements and design specifications for the system, and provide the basis for the main research and technological activities of the project. - WP2: User centred design
Coordinate the system development efforts by means of an iterative user centred design approach, and run in parallel with WP3, WP4, WP5 and WP6, where the technology necessary to accomplish XoSoft will be developed. - WP3: Smart and soft sensing, and actuation
Focus on new technologies for sensors and actuators based on smart materials and advanced textiles. - WP4: Interaction and control
Develop the control of the system, including identification of user motion and intention. - WP5: Integration and testing
Centered on the integration and testing of the system in a laboratory environment. - WP6: Monitoring and feedback
Provide the monitoring and feedback system. - WP7: Validation and user needs
Evaluate the mature prototype in clinical and home trials.